What is the Smear Test?
The smear test is used primarily in cervical cancer, cellular irregularity and cancer symptom infections in the cervix. With this test, cellular disorders can be detected earlier and the risk of uterine and cervical cancer can be easily controlled. Cervical cancer is known as the most common type of cancer seen in women.
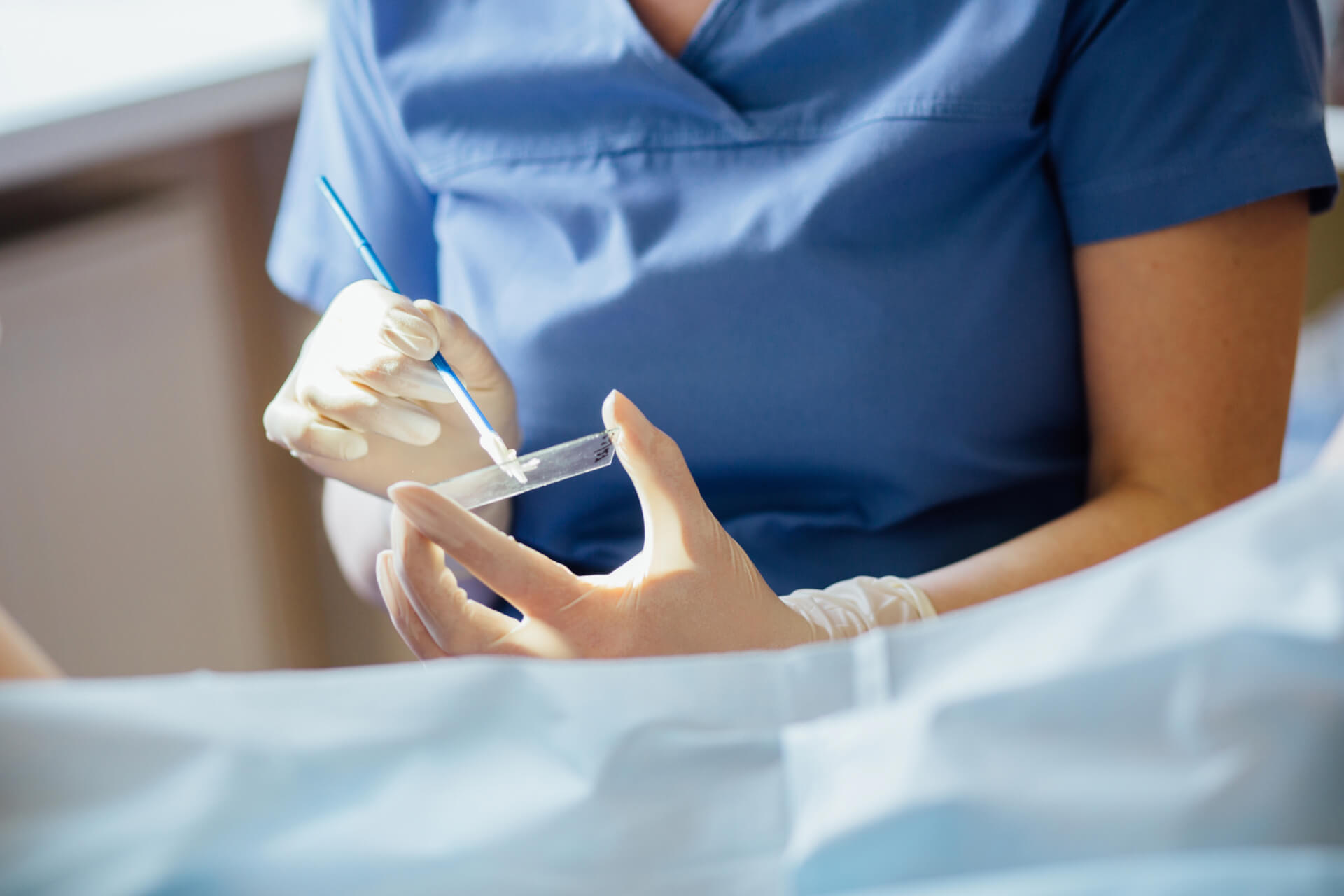
The disease is often caused by reasons such as starting sexual intercourse at an active age, HPV infection, vitamin A level and many partners. Therefore, testing plays an important role in screening for cervical cancer. Myrtle smear test is a very simple and painless procedure. By taking a swab from the cervix area with the help of a brush, cell samples are collected and the test is performed. Afterwards, the sample is examined by the pathologist with a microscope tool to see if there is any abnormal development.
If the test is positive, the obstetrician requests HPV test or colposcopy from the patient. This test is not done during the menstrual period, and the best time is 10-20 days after the menstrual period. The main goal of this test is not to detect a possible cancer, but to detect precancerous lesions that are not cancer but have the potential to transform into cancer. Before the smear is taken, no sexual intercourse should be established within 48 hours and the vagina should not be washed.
Why is the Smear Test Done?
Myrtle smear test
Myrtle smear test is applied to find out if there are abnormal cells occurring in the cervix and intrauterine membrane region, or if there are, at what stage they are. But the smear test is not just about cancer. Although it is of great importance in the diagnosis of a serious disease such as cervical cancer, it is also used in the diagnosis of changes in the uterus caused by infectious diseases.
This test provides early detection of cancer precursor cells and treatment in a short time depending on the patient’s health status. With early diagnosis, treatment is applied by preventing the progression of cancer tissues. Thanks to early diagnosis, patients can be protected from the effects of cervical cancer and regain their health with appropriate treatment methods. In addition, the process of getting the result varies according to the place where you have it done.
Risk Factors for Cervical Cancer and Precursor Lesions
- Early First Sexual Experience
- Smoking
- Having A Low Education Level
- Long-Term Use Of Birth Control Pills
- A Diet Low İn Vegetables And Fruits
- Overweight
- İmmune System Deficiency
- HIV İnfection
- Cervical Cancer İn Mother Or Sister İn The Family
- Not Having A Routine Smear Test
- Having A History Of Sexually Transmitted Herpes Virus And HPV
- Advanced Age
- Race (Blacks Are More At Risk)
- Origin Of Asia, Africa And Latin America
- Early First Gestational Age
- Having More Than One Pregnancy
- Diet Deficient İn Folic Acid, Vitamin A And Vitamin C
- Having Too Many Sexual Partners Of The İndividual Or Their Spouse
- Genital Wart
- Poor Genital Care
When Should a Smear Test Be Started?
The smear test should be started 3 years after the first sexual experience or after the age of 21. Women younger than 30 should have a smear once a year. For women older than 30 years of age, the smear test should be repeated every 2 or 3 years if the result of 3 consecutive smears is negative. However, the frequency of screening should be increased in those who appear to be HIV-positive, have a deficient immune system, use estrogen, and undergo organ transplantation.
Since the smear test is a screening test, colposcopy, biopsy and cervical curettage may be required when suspicious results are obtained. Cervical cancer usually occurs between the ages of 35-55. However, it is rare in women under the age of 20.
For detailed information on the subject, you can contact us and watch our related content:



No comment yet, add your voice below!